Why Top Cement Manufacturers Are Rushing To Meet Wastewater Compliance - And What You’ll Miss if You Don’t
Executive Summary
The cement industry in India faces stringent wastewater compliance regulations that require comprehensive understanding and implementation of best practices. With the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) enforcing strict discharge standards and the National Green Tribunal (NGT) increasing oversight, cement manufacturers must prioritize environmental compliance to maintain operational licenses and avoid penalties.
Understanding the Regulatory Landscape
Key Regulatory Framework
India's wastewater management regulations for the cement industry are governed by multiple legislative acts and enforcement bodies. The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974 serves as the foundational legislation, establishing the CPCB and State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs) as primary enforcement agencies.
The regulatory framework includes:
Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) - Sets nationwide effluent standards and technical guidelines
State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs) - Enforce compliance at state level with region-specific adaptations
National Green Tribunal (NGT) - Issues directives and enforces penalties for violations
Recent Regulatory Updates
The 2024 Liquid Waste Management Rules introduced by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change mark a significant evolution in wastewater regulations. These rules mandate:
Extended User Responsibility (EUR) framework for bulk water consumers
Initial reuse targets of 20% for 2027-28, rising to 50% by 2030-31
Rigorous compliance framework with monthly reporting requirements to SPCBs
Compliance Table
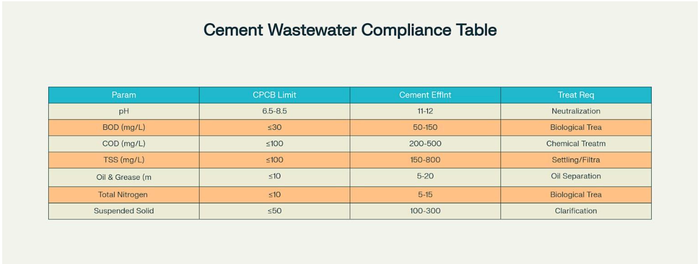
Wastewater Parameters and CPCB Compliance Standards for Cement Industry
Wastewater Parameters and Compliance Standards
Critical Parameters for Cement Industry
Cement plants must monitor and control several key wastewater parameters to ensure regulatory compliance. The industry typically generates wastewater from cooling operations, equipment washing, and dust suppression activities [7] [8] .
Primary Compliance Parameters:
pH levels : CPCB standard range of 6.5-8.5, while cement effluent typically shows 11-12 due to alkaline dust
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) : Standard limit ≤30 mg/L
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) : Standard limit ≤100 mg/L
Total Suspended Solids (TSS) : Standard limit ≤100 mg/L
Oil and Grease : Standard limit ≤10 mg/L
Treatment Requirements
Each parameter requires specific treatment approaches:
pH Neutralization : Essential for alkaline cement effluent using acid dosing or CO₂ injection
Biological Treatment : Required for BOD and COD reduction
Physical Treatment : Settling tanks and clarifiers for TSS removal
Chemical Treatment : Coagulation and flocculation for fine particle removal
Best Practices Implementation in Cement Industry
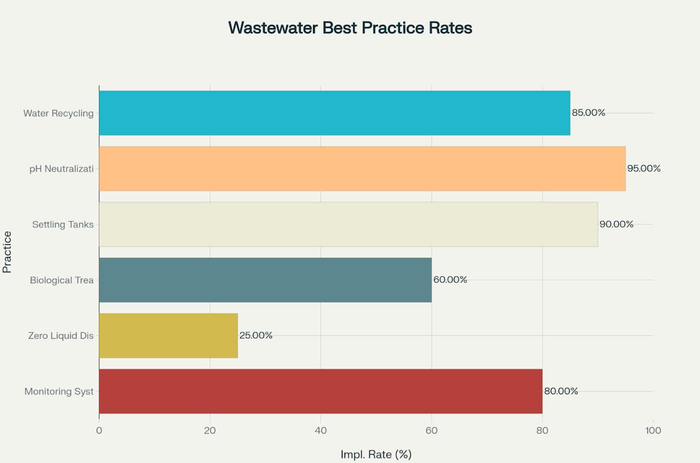
Wastewater Best Practice Rates
Implementation Rates of Wastewater Treatment Best Practices in Cement Industry
Water Recycling and Reuse
The Indian cement industry has made significant progress in water management, with 99% of installed capacity using dry process manufacturing to minimize water consumption. Leading companies like UltraTech have implemented comprehensive water conservation strategies:
Rainwater harvesting : 85 lakh cubic metres harvested at Vikram Cement Works in FY20
Zero-water discharge policy across all facilities
Concrete recycling technology : UltraTech saved 100 million litres through 'baton wash' technology
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) Systems
ZLD technology represents the most advanced approach to wastewater management, achieving complete water recovery with only solid waste for disposal ] . Implementation involves:
Pre-treatment : Screening and pH adjustment
Advanced Treatment : Reverse osmosis, nanofiltration, electrodialysis
Concentration and Evaporation : Thermal processes for water recovery
Solid Waste Management : Appropriate disposal of concentrated residues
Monitoring and Control Systems
Effective compliance requires robust monitoring systems with:
Continuous monitoring of effluent parameters
SCADA systems for automated control
Regular sampling and testing as per SPCB requirements
Data logging and reporting for regulatory compliance
Compliance Costs and Implementation Timeline
Investment Requirements
Wastewater treatment infrastructure requires significant capital investment across different treatment levels:
Primary Treatment : ₹0.5-2.0 crores (3-6 months implementation)
Secondary Treatment : ₹2.0-5.0 crores (6-12 months implementation)
Tertiary Treatment : ₹3.0-8.0 crores (12-18 months implementation)
Zero Liquid Discharge : ₹10.0-25.0 crores (18-36 months implementation)[Based on industry data]
Return on Investment
Despite high initial costs, proper wastewater management delivers:
Regulatory compliance avoiding penalties and shutdowns
Water cost savings through recycling and reuse
Environmental benefits supporting sustainability goals
Operational efficiency through process optimization
Evolution of Regulatory Environment
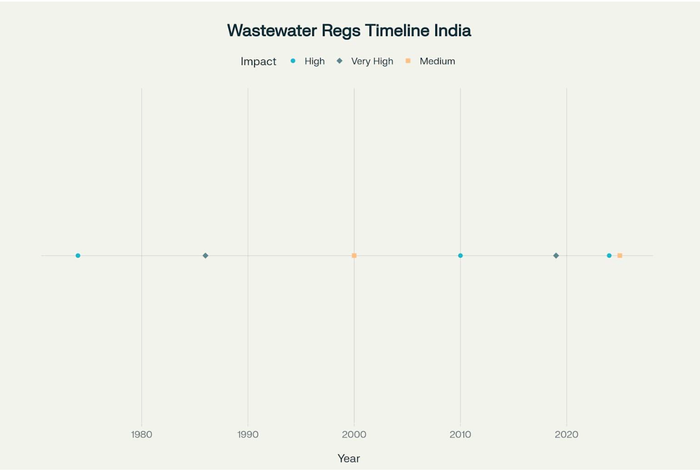
Wastewater Regulation Timeline
Evolution of Wastewater Regulations for Cement Industry in India (1974-2025)
Historical Development
The regulatory landscape has evolved significantly since 1974, with major milestones including:
1974 : Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act established foundation
1986 : Environment Protection Act expanded regulatory scope
2019 : NGT amended sewage treatment standards
2024 : Liquid Waste Management Rules introduced comprehensive framework
2025 : Enhanced monitoring requirements implemented
Future Regulatory Trends
Emerging trends indicate:
Stricter discharge standards with lower permissible limits
Mandatory ZLD implementation for water-stressed regions
Digital monitoring requirements with real-time data transmission
Extended producer responsibility for water lifecycle management
Carbon footprint integration linking water and climate compliance
Case Studies: Successful Implementations
BlueDrop Project Overview

Deccan Cement Project
Client: Deccan Cements Limited (DCL), established in 1979.
Objective: Sustainable wastewater management for industrial & residential effluent.
Location: Bhavanipuram, Hyderabad, Telangana.
System Commissioned: January 2021, operational to present.
Technology: Aerated Vertical-Flow Constructed Wetlands (Natural Treatment System).
Capacity: 1.2 MLD (million liters/day) .
Technology Highlights
Artificial Aeration: Boosts oxygen availability, accelerates pollutant breakdown.
Performance:
BOD removal improved 10x ; TN/TP removal 2–4x vs passive systems.
Land Efficiency: Uses 1/5th less land than conventional wetlands .
Design & Process
Primary Treatment: Bar screening → equalization → anaerobic chambers.
Secondary Treatment:
Two constructed wetland units (1000 m² each, 1.8 m depth).
Layers of gravel, plant roots, microbial communities for nutrient removal.
Water Reuse: Treated water recycled for cement operations, dust suppression, landscaping .
Treatment Performance
Influent vs Effluent (Major Reductions):
BOD: 274 mg/L → 9.8 mg/L ( 96.4% reduction ).
COD: 505 mg/L → 58.6 mg/L.
TSS: 620 mg/L → 45.6 mg/L.
Total Nitrogen: 73.4 mg/L → 10.6 mg/L.
Overall Organic Removal Efficiency: 95–96% .
Nutrient Removal
TN Reduction: 87% via nitrification-denitrification.
Phosphorus Reduction: 86.5%, due to phosphate-accumulating microbes .
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Total Cost: ₹6.12 crore (CAPEX + OPEX).
Benefit-Cost Ratio (BCR): 7.61 – highly profitable.
Payback: 1.89 years (less than 2 years).
Economic Viability: Significant ROI driven by water reuse and compliance .
Co-Benefits
Low energy consumption & carbon footprint.
Silent, odor-free operation.
Sludge-free and simple maintenance.
Long system life with variable load handling.
Technology Solutions and Innovations
Advanced Treatment Technologies
Modern cement plants employ multiple treatment technologies:
Membrane bioreactors (MBR) for high-quality effluent production
Moving bed bioreactors (MBBR) for compact biological treatment
Activated sludge processes for large-scale operations
Advanced oxidation processes for recalcitrant pollutants
Digital Monitoring Solutions
Industry 4.0 technologies enhance compliance through:
IoT sensors for real-time parameter monitoring
AI-driven predictive analytics for treatment optimization
Blockchain for transparent compliance reporting
Remote monitoring systems reducing operational costs
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon Footprint Considerations
Wastewater treatment in cement industry intersects with climate goals:
Energy consumption in treatment processes affects carbon footprint
Water recycling reduces pressure on freshwater resources
ZLD systems support circular economy principles
Renewable energy integration in treatment plants reduces emissions
Ecosystem Protection
Proper wastewater management protects:
Surface water bodies from industrial contamination
Groundwater aquifers from infiltration of pollutants
Soil quality in surrounding agricultural areas
Biodiversity in downstream ecosystems
Implementation Roadmap for Cement Plants
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning (Months 1-3)
Conduct comprehensive wastewater audit
Identify compliance gaps against CPCB standards
Develop treatment technology selection criteria
Prepare regulatory approval applications
Phase 2: Infrastructure Development (Months 4-18)
Install primary and secondary treatment systems
Implement monitoring and control systems
Train operational staff on new procedures
Establish quality assurance protocols
Phase 3: Advanced Systems (Months 19-36)
Deploy tertiary treatment or ZLD systems
Integrate digital monitoring solutions
Optimize treatment processes for efficiency
Achieve full regulatory compliance certification
Phase 4: Continuous Improvement (Ongoing)
Regular system audits and upgrades
Technology optimization for cost reduction
Sustainability reporting and transparency
Industry best practice sharing
Conclusion
Compliance in wastewater management for India's cement industry requires a comprehensive approach combining regulatory understanding, nature based solutions, technological implementation, and operational excellence . With evolving regulations and increasing environmental scrutiny, cement manufacturers must proactively invest in advanced treatment technologies and robust monitoring systems.
The industry's transition toward water-positive operations through recycling, reuse, and zero liquid discharge systems demonstrates the potential for sustainable growth. Success depends on strategic planning, stakeholder engagement, and continuous adaptation to regulatory changes.
As the cement industry continues to grow with India's infrastructure development, maintaining environmental compliance while optimizing operational efficiency will determine long-term competitiveness and sustainability. Companies that embrace advanced wastewater management practices today will be better positioned for future regulatory requirements and market demands.
The integration of digital technologies, circular economy principles, and community engagement creates opportunities for cement manufacturers to transform wastewater management from a compliance burden into a competitive advantage, supporting India's vision of sustainable industrial development. BlueDrop Waters is uniquely positioned to help implement effective wastewater and effluent management strategies with expertise in all three areas. Reach out to get a free compliance audit.
⁂
Sources:
https://aquamech.co.in/industrial-wastewater-treatment-compliance-in-india/
https://susbio.in/government-standards-and-guidelines-for-sewage-treatment-plants-stps-in-india-2025-expert-guide/
https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2018-07/documents/cement_mfg_dd_1974.pdf
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/exploring-indias-legal-framework-industrial-4z83f
https://www.hecspstp.com/regulations-for-sewage-treatment-plants-in-india/
https://www.epa.gov/eg/cement-manufacturing-effluent-guidelines
https://www.downtoearth.org.in/water/there-are-challenges-and-opportunities-in-indias-2024-liquid-waste-management-rules
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1796222
https://www.nexi.go.jp/en/environment/pdf/ins_kankyou10e.pdf
https://www.netsolwater.com/how-does-government-policy-and-regulation-shape-wastewater-treatment-practices-in-indian-industries.php?blog=5695
https://www.ppsthane.com/blog/cpcb-wastewater-discharge-standards
https://www.holcim.com/sites/holcim/files/documents/lafargeholcim_cement_environmental_directive_revison_2020.pdf
https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/chandigarh/ngt-panel-spots-green-compliance-gaps-at-adani-group-cement-plant/articleshow/118095507.cms
https://www.netsolwater.com/cpcb-guidelines-for-cement-industry.php?blog=4181
https://www.ecomena.org/environment-mena-cement/
https://www.cpcb.nic.in/uploads/Projects/Hadzardous-Waste/Latest_51_Latest_51_GUIDELINES-ON_CO-ProcessinginCement.pdf
https://cpcb.nic.in/generalstandards.pdf
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2352710223022581
https://www.taxtmi.com/article/detailed?id=14127
https://cpcb.nic.in/effluent-emission/
https://www.oemupdate.com/technology/water-treatment-for-cement-plant/
https://www.tespl.com/projects/water-conservation-and-recycling/cement-and-steel-plants.php
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9477945/
https://www.getchemready.com/water-facts/concrete-wastewater-treatment/
https://www.saltworkstech.com/articles/what-is-zero-liquid-discharge-why-is-it-important/
https://www.internationaljournalcorner.com/index.php/ijird_ojs/article/download/135524/94648/326076
https://samcotech.com/solutions/zero-liquid-discharge/
https://www.ncbindia.com/environmental-management.php
https://sensorex.com/concrete-waste-disposal-managing-wastewater/
https://canadianclear.com/zero-liquid-discharge.html
